Transforming your organization’s maintenance practices and achieving optimal operational efficiency is a journey that involves careful planning and strategic execution. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emerges as a robust framework to guide this transformative endeavor. By encompassing a series of well-defined steps, TPM empowers your team to elevate equipment/process reliability, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity. Let’s delve into the traditional eight step process that paves the way to successful TPM implementation.
The 8 Steps to Total Productive Maintenance Rollout
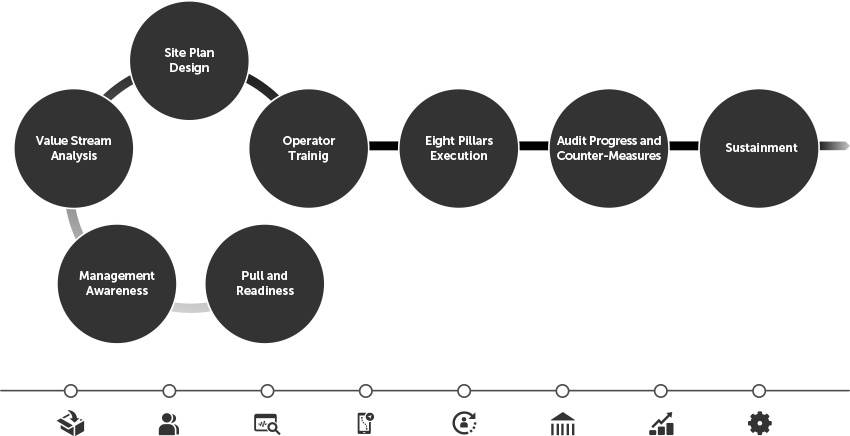
| ➢ | Step 1: Pull and Readiness – Begin your TPM journey by igniting a sense of urgency around its adoption. This step involves communicating the substantial benefits TPM offers while securing top management’s commitment to allocate necessary resources like training and equipment. A strong foundation of support is key to propelling TPM success. |
| ➢ | Step 2: Management Awareness – Ensuring clarity and comprehension among site leadership, managers, and supervisors is pivotal. This step imparts an understanding of TPM, their roles within the transformation, and how TPM aligns with performance objectives. Additionally, they will grasp the crucial concept of the six equipment-related losses and how TPM can be used to eliminate them. |
| ➢ | Step 3: Value Stream Analysis – The third step involves identifying and understanding key value streams within your organization. Analyzing existing value streams, assessing the current state of key equipment operating conditions and plant-wide maintenance practices, and determining the potential impact of improving the six equipment-related losses. |
| ➢ | Step 4: Site Plan Design – This step involves creating your unique TPM Implementation Plan to include specific goals, objectives, and milestones. |
| ➢ | Step 5: Operator and Support Staff Training – Empower operators and support staff through comprehensive TPM training. This step involves training on the TPM principles and practices that are relevant to their roles. Reviewing the new-normal for equipment conditions, performance, maintenance, process ownership, and routine equipment care. |
| ➢ | Step 6: Eight Pillars Execution – This step involves executing the TPM Pillars per your site-specific implementation plan, including autonomous maintenance, maintenance improvement, and focused equipment improvement—all while continuing to develop the competencies of site leadership, support staff, and operators. This includes developing capabilities in applying standard work, predictive and preventive maintenance techniques, problem-solving, waste elimination, EH&S compliance, etc. |
| ➢ | Step 7: Audit Progress and Countermeasures – Regularly assess your implementation plan’s progress. Create needed countermeasures to close gaps, conduct audits to assess the effectiveness of the implementation and identify areas that need enhancement. |
| ➢ | Step 8: Sustainment – The final step ensures the continuity of your TPM practices. Establish standard work routines and Gemba walk practices to perpetuate progress. This ongoing approach nurtures a culture of continuous improvement, backed by top management’s ongoing support. |
Successful TPM implementation yields heightened equipment reliability, reduced costs, and increased productivity. Moreover, it nurtures robust relationships between people and equipment, uniting all levels of your organization toward a common reliability goal. The outcome? A data-driven process enhancing flexibility, controlling costs, and fostering a safe and satisfying environment that aligns with your strategic objectives.
